In order for foreign nationals to work in Japan, they must obtain a status of residence that allows them to work.
Even if the representative of the company is a foreigner, if the company is hiring a foreigner to work in Japan, the foreign staff must obtain a status of residence that allows them to work.
The status of residence in Japan is divided into different types according to the job description.
In principle, the status of residence for employment must be full-time employment.
In a part-time job, it will be difficult to obtain residency status for work.
If you want your foreign staff to work as a part-time, hire foreign students, people with family residence status, or people with residence status without work restrictions.
The common status of residence for employment is as follows.
・Engineer/ Specialist of Humanities/ International Services
・Intra-company Transferee
・Highly Skilled Professional(1)
Engineer/ Specialist of Humanities/ International Services
There are a wide range of jobs that fall under this status of residence.
Specific examples include the following
- Sales
- advertising
- Trade affairs
- System Engineer
- Design and development of precision machinery and equipment, etc.
- designner
- interpreter
Requirements of Engineer/ Specialist of Humanities/ International Services
1: There must be an employment contract between the employer and the foreign staff member.
If you work in a Japanese branch or representative office, you will sign a contract with a company in your home country.
2: One of the following conditions applies.
A: Knowledge relevant to the job description must have been acquired through college or university .
B: At least 10 years of work experience in the job description in which they are engaged.
At least 3 years of work experience is required for some jobs such as interpretation and translation.
3: The remuneration must be equal to or greater than the remuneration received by Japanese workers
In Japan, the minimum wage is set by law.
Salaries below the minimum wage will not be allowed.
4: The state of the company’s operations
Companies are judged to see if they can hire and pay their employees.
If the business requires a business license, it will also be checked to see if it is legally licensed.
5:The behavior of foreign staff is good.
International students and foreigners with family stays can work up to 28 hours a week.
If it is found that they have been working more than the legally mandated hours, they will be deemed to be misbehaving.
If that happens, it will not be allowed.
Intra-company Transferee
If you are transferred from an overseas head office to a Japanese branch, subsidiary or representative office, you can apply for “Intra-company Transferee”.
The jobs that can be worked by “Intra-company Transferee” are those that fall under the category of “Engineer/ Specialist of Humanities/ International Services”.
Requirements for Intra-company Transferee
1: You have been working at an overseas head office for more than one year in a “Engineer/ Specialist of Humanities/ International Services” type of job.
2: The remuneration must be equal to or greater than the remuneration received by Japanese workers.
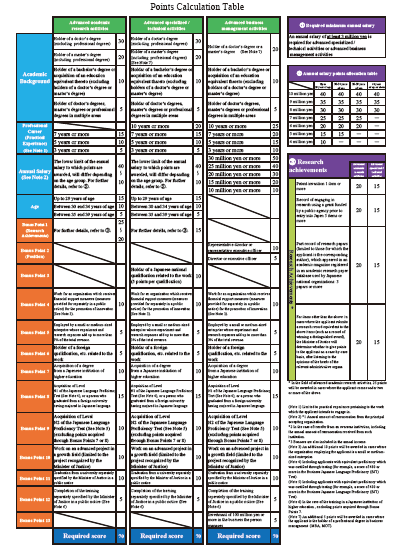
Highly Skilled Professional(1)
This is a status of residence for foreigners with advanced skills, knowledge and experience.
Compared to other residence statuses for work, there are various preferential measures.
There are three types of Highly Skilled Professional(1), depending on the nature of their work.
A: Advanced academic research activities
b: Advanced specialized/technical activities
C: Advanced business management activities
Requirements for Highly Skilled Professional(1)
1:You must have scored at least 70 points in the points table below.
2: Annual income of \3,000,000- or more
Preferential treatment for Highly Skilled Professional(1)
1. Permission for multiple activities
2. Grant of the “5 years”period of stay
3. Easing of requirements for permanent residence
4. Permission for the spouse of the highly-skilled foreign professional to work
5 .Permission for bringing a parent(s) to accompany the highly-skilled foreign professional to Japan under certain conditions
6. Permission for a domestic worker to accompany the highly-skilled foreign professional to Japan under certain conditions
7. Preferential processing of entry and residence procedures